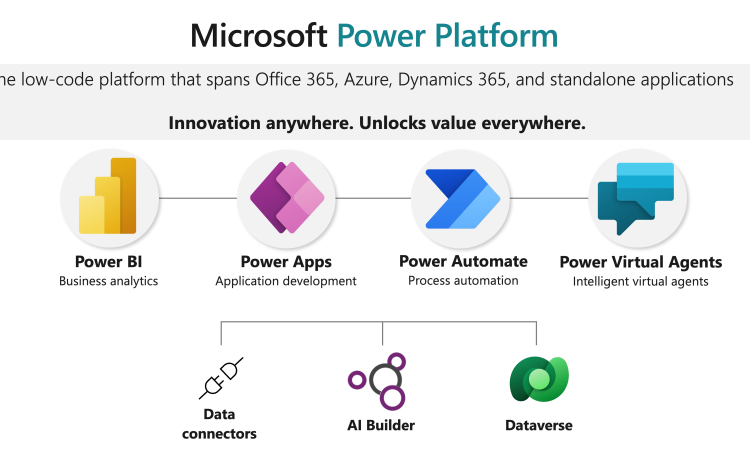
Microsoft Power Platform is an inclusive technology, revolutionizing the entire software design process. Its ease-of-use creates a culture of innovation, helping you realize untapped value you couldn’t access before.
What is Low Code Development?
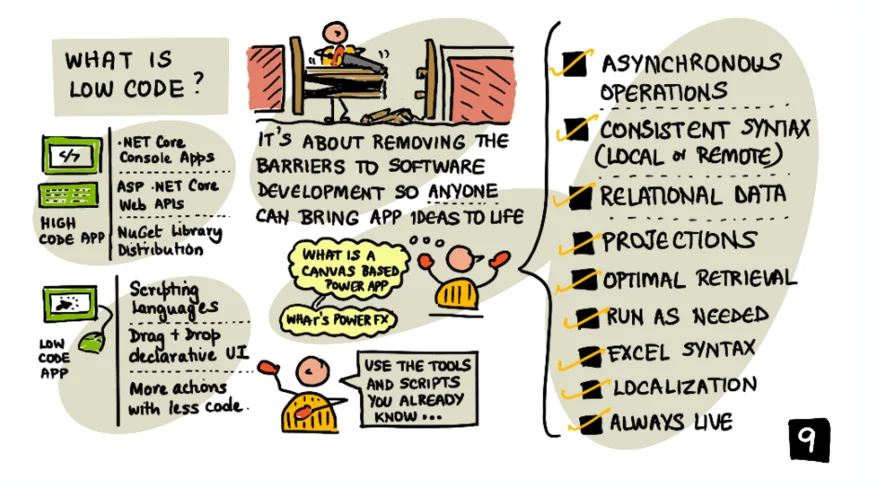
Low-code development differs from traditional coding in that it allows users to create applications and workflows with little or no coding required. In low-code development, users leverage pre-built visual blocks and templates to create applications, automations, and workflows, which can be quickly modified or extended to meet specific requirements. Traditional coding, on the other hand, involves writing custom code from scratch, which can be time-consuming and requires significant programming expertise.
While some level of coding knowledge can be helpful in low-code development, it is not necessary. With low-code platforms like Power Platform, people with little to no coding experience can use drag-and-drop visual interfaces to create applications, automations, and workflows. These visual interfaces often include pre-built components and connectors that enable users to quickly create complex business solutions.
Low-code development is designed to democratize software development, making it accessible to more people within an organization. By allowing business users to create their own applications and workflows, low-code development can reduce the workload on IT departments and help organizations to quickly respond to changing business needs.
Low-code development is a different approach to software development that allows users to create applications and workflows with little or no coding required. While some level of coding knowledge can be helpful, it is not necessary, and people with little to no coding experience can still use low-code platforms like Power Platform to create custom business solutions.
What are Power Platforms?
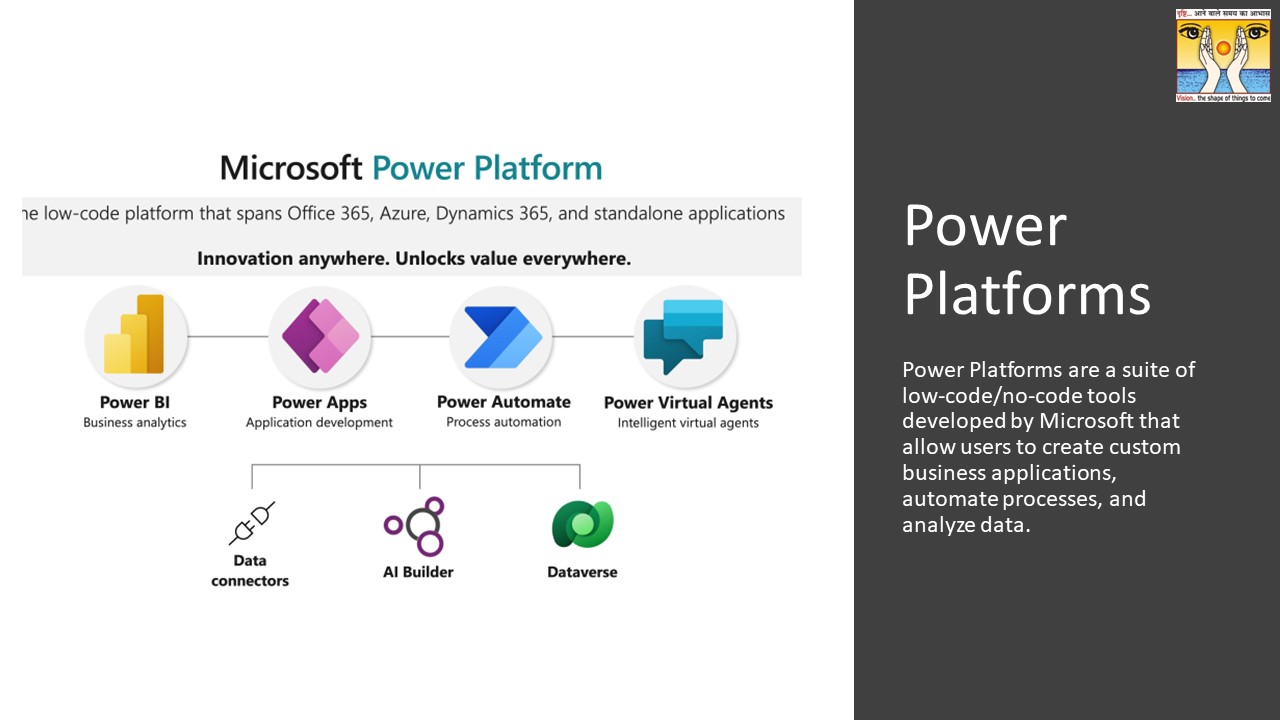
Power Platforms are a suite of low-code/no-code tools developed by Microsoft that allow users to create custom business applications, automate processes, and analyze data.
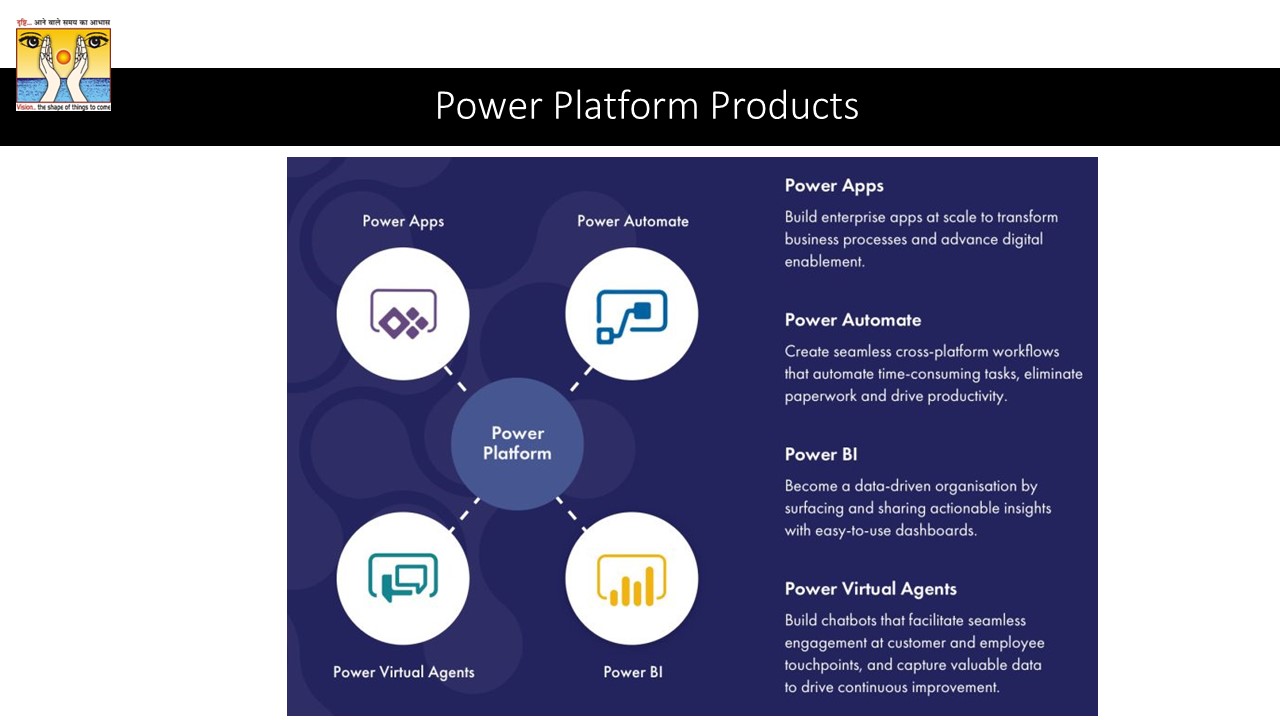
Various Products under Power Platform Suite
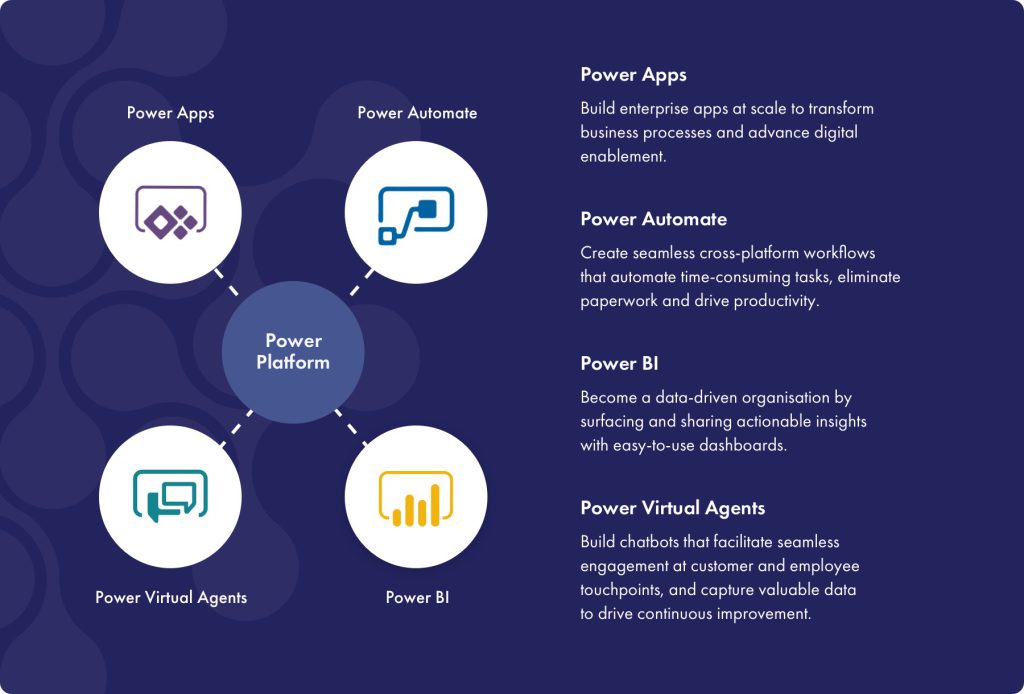
- Power Apps,
- Power Automate,
- Power BI,
- Power Pages
- Power Virtual Agent
Do more with less by using low-code tools to adapt
Accelerate innovation and reduce costs as you analyse data, automate processes, and build apps, websites, and virtual agents with Power Platform; all with limited coding!
Use of Power Platforms
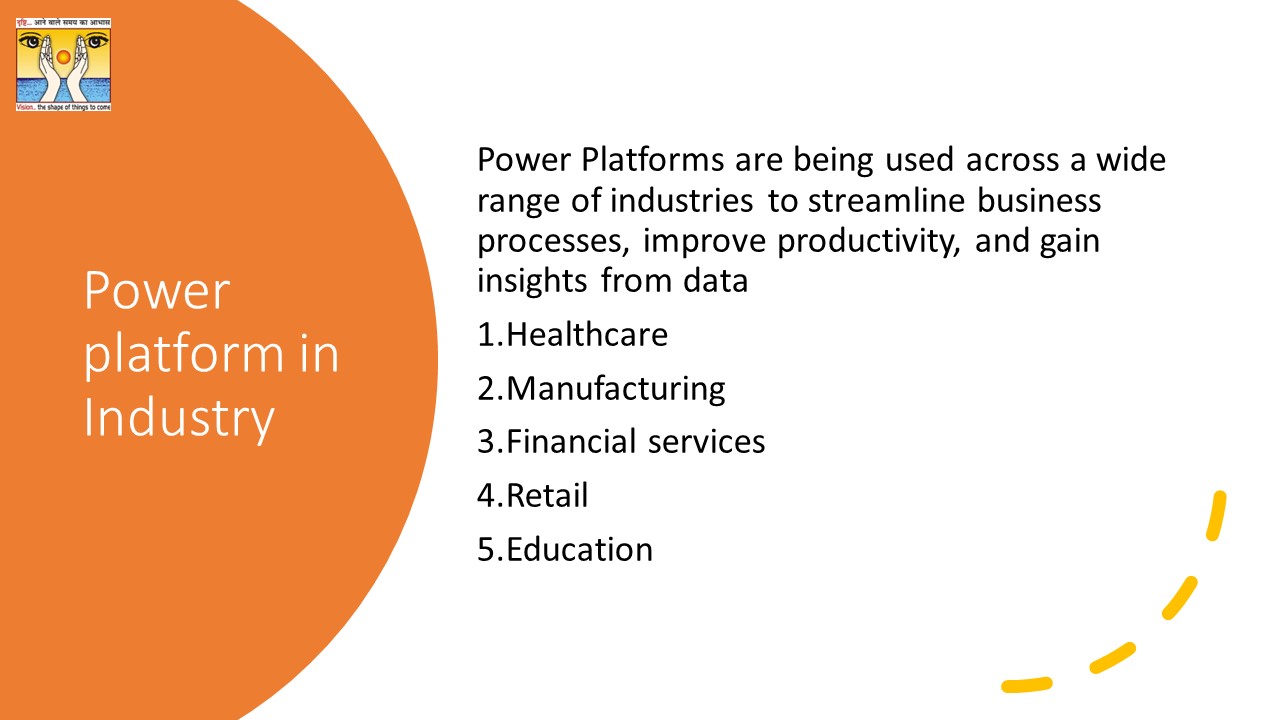
Power Platforms are being used across a wide range of industries to streamline business processes, improve productivity, and gain insights from data. Here are some examples of how different industries are using Power Platforms:
- Healthcare: Healthcare organizations are using Power Platforms to create custom applications to manage patient data, track medical equipment, and monitor supply chain inventory. They are also using Power BI to analyze medical data and identify patterns that could lead to better patient outcomes.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers are using Power Platforms to automate processes, such as tracking inventory, scheduling production runs, and monitoring equipment maintenance. They are also using Power BI to analyze production data and identify areas for process improvements.
- Financial services: Financial services companies are using Power Platforms to automate loan approvals, create custom financial reports, and monitor fraud and risk. They are also using Power BI to analyze financial data and identify trends and patterns that could lead to better business decisions.
- Retail: Retailers are using Power Platforms to create custom applications to manage inventory, track customer orders, and monitor supply chain logistics. They are also using Power BI to analyze sales data and identify areas for growth and improvement.
- Education: Educational institutions are using Power Platforms to automate administrative tasks, such as student enrollment, attendance tracking, and grading. They are also using Power BI to analyze student data and identify areas for improvement in academic performance and retention.
Overall, Power Platforms are being used to streamline processes, improve productivity, and gain insights from data across many industries. The flexibility and versatility of the tools make them useful for a wide range of applications and use cases.
Advantages of using Power Platform over traditional coding methods
Power Platform’s low-code/no-code approach offers businesses several advantages over traditional coding methods, including faster time-to-market, lower development costs, faster innovation, easier integration with other tools and services, and automatic updates.
First, Power Platform’s low-code/no-code approach makes it accessible to users with varying technical skills, allowing more people to participate in creating custom business solutions. This means that businesses can reduce their reliance on IT departments or external developers to create apps, resulting in faster time-to-market and lower development costs.
Second, Power Platform enables rapid prototyping and iteration, making it easier for users to create, test, and refine their applications in real-time. This results in quicker feedback cycles and faster innovation, which is especially important in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Third, Power Platform provides built-in connectors to a wide range of data sources and services, allowing users to easily integrate their applications with other tools and services. This helps to streamline workflows and reduce data silos, resulting in more efficient business processes.
Further, Power Platform’s cloud-based architecture enables automatic updates and ensures that users are always working with the latest version of the software. This means that businesses can focus on developing their applications rather than worrying about maintaining infrastructure and software updates.
Role of AI in Low Code Developments
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to greatly enhance low-code development by automating various aspects of the development process. One way AI can help is by using machine learning algorithms to automate the creation of code snippets, reducing the amount of manual coding required.
In addition, AI can be used to assist with the testing and debugging of low-code applications, by automatically identifying errors and recommending fixes. This can help to reduce the time and effort required for testing and ensure that applications are more reliable.
AI can also be used to help identify patterns in data, which can then be used to create predictive models or identify opportunities for optimization. This can help organizations to make data-driven decisions and automate workflows based on data insights.
Power Platform has already started incorporating AI capabilities into its low-code platform. For example, Power Apps AI Builder allows users to easily incorporate pre-built AI models into their applications. AI Builder includes pre-built models for things like object detection, text recognition, and sentiment analysis, which can be easily integrated into applications without the need for coding.
Power Platform also includes capabilities for automatically generating code based on user input, which can be useful for creating simple applications quickly. Additionally, Power Platform has integrated AI-driven insights and recommendations throughout the platform, providing users with actionable insights to help optimize their applications.
Overall, AI has the potential to greatly enhance low-code development, and Power Platform is already incorporating AI capabilities to help users create applications more quickly and easily.
Products similar to Power Platforms
There are a number of other low-code/no-code platforms that offer similar capabilities to Power Platforms. These include platforms like Google Cloud AppSheet, Zoho Creator, and Salesforce Lightning, which enable users to create custom business applications without needing to write code. Additionally, there are a variety of analytics and data visualization tools, like Tableau and Qlik, which enable users to analyze data and create interactive reports and dashboards. While these platforms may offer some similar capabilities, Power Platforms provide a suite of tools that are tightly integrated with other Microsoft services like Office 365 and Dynamics 365, making it a popular choice for organizations that already use these services.
You say Low, I say Code!
- What is Low Code?
- How are the Benefits?
- What does Power Platform Provide?
- How can we extend Power Platform?
Limitations of Power Platform
While Power Platform offers many benefits, there are some limitations to be aware of:
- Customization limitations: While Power Platform offers a lot of flexibility, there are some limitations to customization. Some complex business requirements may require more advanced development work outside of Power Platform.
- Data integration limitations: Power Platform can connect to a wide variety of data sources, but some sources may not be supported. There may be cases where data needs to be migrated or integrated with other systems, requiring additional development work.
- Limited performance scalability: Power Platform’s performance can be impacted if the number of users, data volume, or complexity of workflows becomes too high. It is important to carefully plan for scale and performance requirements.
- Limited control over infrastructure: With a cloud-based service like Power Platform, users have limited control over the infrastructure and may not be able to customize certain aspects of the environment.
- Limited offline capabilities: Power Platform is primarily an online service, and while there are some limited offline capabilities, some functionality may not be available when offline.
- Licensing costs: While Power Platform offers a free version, more advanced features and capabilities may require a paid subscription. The cost of licensing can add up over time, especially for large organizations.
In summary, while Power Platform offers many benefits and is a powerful tool for creating custom business solutions, it is important to be aware of its limitations, including customization, data integration, scalability, infrastructure control, offline capabilities, and licensing costs.
References
- LowCodeFebruary#
- Microsoft Power Platform Page
- What is Microsoft Power Platform
- Power Platform Documentation
- Power Platform Blog